Elements of narrative
1. Before you scroll through the rest of the page, take 5 minutes to watch this overview video:
2. Then, use the site content list to navigate the page.
Characters
The people, animals, or personified things in the story
The character who creates CONFLICT for the main character
HOW the a DYNAMIC character changes.
A character who CHANGES as a result of the conflict
A character who STAYS THE SAME throughout the story
The 5 Ways of Characterization
How the author "paints" the character
Point of View
Narrator = the character or "voice" who's telling the story.
1st Person Point of View
The narrator is a character in the story
3rd Person Point of View
The narrator is NOT a character in the story
To figure out the POINT OF VIEW of a story, ask yourself: "WHO is telling the story?"
Setting
The time and place of a story
❝
Kino awakened in the near dark. The stars still shone and the day had drawn only a pale wash of light in the lower sky to the east. The roosters had been crowing for some time, and the early pigs were already beginning their ceaseless turning of twigs and bits of wood to see whether anything to eat had been overlooked. Outside the brush house in the tuna clump, a covey of little birds chittered and flurried with their wings.
from The Pearl
❝
We lived in a time of drought and war. The great empires had fallen and been divided. The land was parched and starved for moisture, and the man who lived on it fought for every drop. Outside, the wind howled like something wounded. Inside, our skin flaked, and our eyes stung and burned. Our tongues were like thick snakes asleep in dark graves.
from The Water Wars
❝
Dodging low tree branches, leaping over dips and cracks in the sidewalk, Cody Carter ran harder and faster down Chimney Rock than he had ever run in his entire life. Someone was chasing him and quickly closing the short gap that lay between them.
from Laugh Till You Cry
Types of Conflict
conflict = the problem or struggle in the story
Internal Conflict
Individual vs. Self
External Conflicts
Individual vs. Individual
Individual vs. Nature
Individual vs. Supernatural
Individual vs. Society
Individual vs. Technology
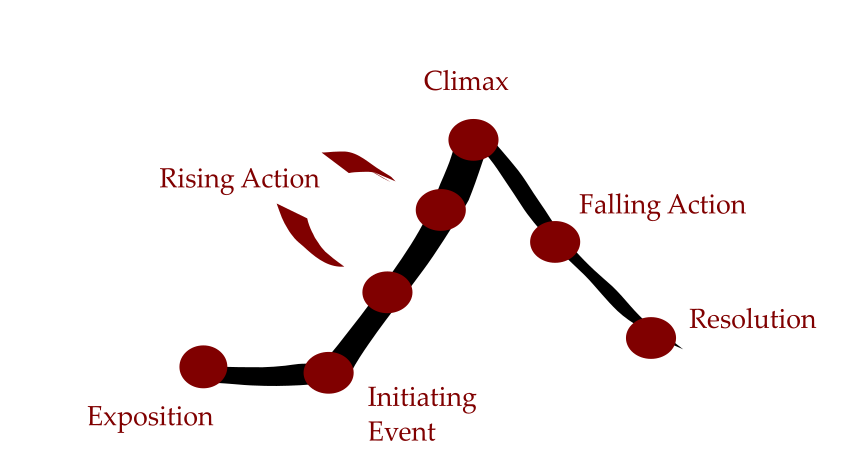
The beginning of the story where the characters and setting are introduced
The conflict is introduced
Suspense builds. This is the BULK of the story. In a 300 page book, at least 250 pages will be rising action.
The high point of the story. This is usually the moment when the protagonist "changes" in some way (changes their mind, beats the bad guy....)
The story starts coming to an end
Any loose ends are tied up. The story comes to an end.
Theme
The lesson or moral of the story
To determine the theme of the story, think about how the protagonist changed (or failed to change) by the end of the story. What lesson did he or she learn? That's usually the theme.
Dialogue
a conversation between two characters in a story
More Narrative Terms

Flashback
A scene in a story that is set in a time EARLIER than the main story. (A jump BACK in time.)

Foreshadowing
The use of clues to hint at coming events in a story

Irony
When the outcome of the story is the exact opposite of what the reader expects or what "should" be.
Once you've read/watched everything on this page, it's time to memorize the terms
